One of two offspring developed in the same pregnancy. The monozygotic twins or identical twins and the dyzygotic or fraternal twins, which develop from two separate eggs fertilized by two separate sperms. Singleton is named to fetus developed alone inside the womb, and generally named for single offspring of a multiple birth.
1) Vanishing Twin
Vanishing Twin (VTS), shown with its umbilical cord near the placenta of its dichorionic diamnotic twin
The vanishing twin is also known as fetal resorption and a fetus in a multi-gestation pregnancy which dies inside the womb or utero and maybe partial or complete reabsorbed twin and also known as twin embolisation syndrome or VTS (Vanishing Twin Syndrome) and fetus papyraceus.
2) Parasitic Twin
Parasitic Twins
Parasitic Twin

Parasitic Twin (twin headed)

Lakshmi Tatma, parasitic twin
The parasitic twin also called the asymmetrical or unequal conjoined twins is the result on vanishing twin pregnancy or conjoined twins.
3) Conjoined Twins
Conjoined Twins , India

Conjoined Twins (body)
Conjoined twins, died after surgical separation
Conjoined twins (other twin is incomplete)
The conjoined twins or Siamese twins are identical twins, where parts of their bodies are joined together in the womb, a rare phenomenon, where the fetus share one of the membrane existing during pregnancy developing between the fetus and the mother called chorion, an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow the nutrients uptake, eliminates the waste and exchange gasses via the mother’s blood supply, called the placenta, and the amniotic sac or the bag of water , the sac where the fetus develops the amniotes.
4) Conjoined Triplets
Siamese Triplets
Conjoined Triplets
5) Mixed Twins
Black and White Twins
Marcia Biggs inherited her mother’s fair complexion, while Millie takes after father Michael, 43, who is of Jamaican origin
The mixed twins are fraternal twins, born with different skin colors and traits from the other twin and considered to be racial features from multi-racial families.
6) Partial Molar Twins or H-Mole pregnancy
Partial Molar Twins or H-Mole pregnancy
Partial Molar Twins
The molar pregnancy or partial molar twins, is a gestational trophoblastic disease or GTD type of pregnancy and can be referred to as complete or incomplete mole. Some studies believe that the cause is a nutritional deficit such as protein or carotene or may be caused by ovulation defect. The molar pregnancy happen when the nucleus of an egg is maybe lost or not active; and the sperms copied itself because the egg lacks genetic information, thus most of the time there is no fetus found, no placenta and no amniotic fluid.
7) Embryonic Twins (Fetus in Fetu Twins)
Embryonic twin from an Iranian man giving birth to his twin
Man with his Embryotic twins
Fetus in Fetu Twins in a child
Fetus in Fetu twin
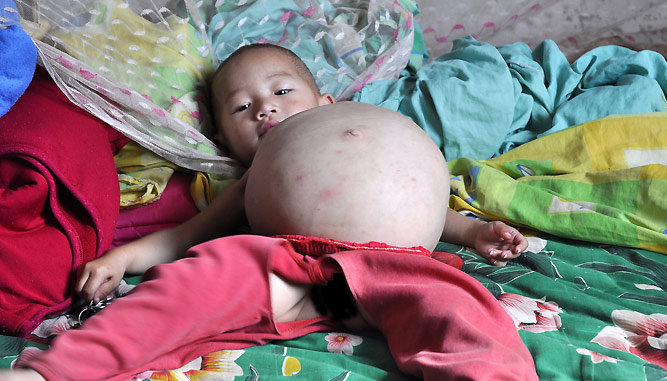
Kang Mengru found parasitic twin inside
The fetus in fetu is an abnormal development in the mass tissue that resembles as a fetus that develop inside the mother’s womb or their twin sister or brother. The first theory of fetus in fetu is that the mass starts as normal fetus, but enveloped inside its twin and the second theory is highly teratoma fetus in fetu, or an encapsulated tumor with tissue elements where some reports said that teratoma consists of hairs, bone, teeth, and very rare organs such as torso or body, eyes, hands and feet and other limbs.
![]() Chimera Twins
Chimera Twins
Lydia Fairchild, Chimera case, “The Twin Inside Me”

Mosaicisms or Blaschko’s Lines (Chimera )
Chimera or Chimerism a theory formed where two fertilized eggs fuse during early childhood development inside the mother’s womb. In the case of Lydia Kay Fairchild, she was pregnant at the time of separation with husband Towsend. Fairchild filed welfare support for her children, but she was required to pass DNA test. The children’s father was positively Jamie Townsend, but she is not the mother of her children. Thus she was accused of surrogacy scam. It was later found out that she have two sets of DNA defining the characteristics as a Chimera or Twin inside her. Mosaicism or Blaschko’s lines is one characteristics of a chimerism.
9) Twin to Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS)
Twin to Twin Transfusion Syndrome
TTTS or Twin to Twin Transfusion Syndrome
TTTS twins

Twin to Twin Syndrome
The Twin to Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS) also called Feto-Fetal Transfusion Syndrome (FFTS) and Twin Oligohydramnios-Polyhydramnios Sequence (TOPS) is a disproportion blood supply that results form high mortality and morbidity. It only occurs in monozygotic or identical twins, which the donor twin is smaller than the recipient twin which are commonly anemic while the recipient twin is often pletoric with hemoglobin differences . It also affect monochorionic multiple pregnancies where the two fetus share a single placenta and common chorion.
10) Monozygotic Twins or Identical Twins
Identical Twins
Identical Twins or Monozygotic Twins
Monozygotic or identical twins are genetically identical having the same genes, and always of the same sex or gender. Identical twins are natural clones.
11) Identical Quadruplets

Identical Quadruplets
Identical Quadruplets, boys
12) Identical Triplets
Identical Triplets

Identical Tirplets celebrated 81st birthday
13) Identical Quintuplets
Identical Quintuplets

Dionne Quintuplets at age 6 years old
14) Fraternal Twins or Dyzygotic

Mary Kate and Ashley Olson , fraternal twins
Fraternal Twins ( Dyzygotic twins)
Fraternal twins also known as sororal twins and dizygotic twins (non-identical or non-similarity twins), tey may look similar but have different looks from each other. Dizygotic twinning is common among older mother to be, and may have different gender (male and female twins).
15) Superfecundation Twins (Twins with Different Father)
Superfecundation Twin
Mother gave birth to twins with different father
Superfetation twins are not really twins according to some studies. The “twins” is conceived a week or more apart . and was developed from separate ovulation and could be from different father or may be same father.
Harriet Mullineux and Thomas are not twins, but are conceived three weeks apart

Grace and Lana twin sisters who were conceived a week apart non identical
16) Ectopic Pregnancy ( fetus grow inside the Fallopian Tube)
Ectopic pregnancy, fetus growing in the fallopian tube

Ectopic Pregnancy – The Time Bomb in the Fallopian Tube
Cullen’s sign, symptoms of Ectopic pregnancy
Cullen’s sign
The ectopic pregnancy also called the tubal pregnancy or eccysis is a pregnancy complications in which the embryo develop outside the uterine cavity, with a rare exceptions, and usually develop in the fallopian tube.
17) Placenta Previa

Salazopyrine In Placenta Previa
Placenta Previa
Placenta praevia or placenta previa AE, is a complications where the placenta is connected to the uterine wall an covering the cervix, occurring usually on the second or third month of pregnancy, but sometimes it can happen on the first trimester and leads to vaginal bleeding or antepartum hemorrhage. The Cullen’s sign, is one symptoms seen patients of ectopic preganncy case.
Placenta Abuptio
Placenta Abruption
Placenta abruptio
Placenta abruption or abruptio placentae, is a pregnancy complications where the placenta (organ that nourishes the fetus inside the womb) separates from its attachment from the uterus wall before the baby is delivered. Pregnant women sufers from vaginal bleeding, premature or abnormal contraction, back pain and abdominal pain, fetal distress and even death.
Abruptio Placenta
Abruptio Placenta, seen after birth

abruptio placenta such abnormal retroplacental hemorrhage prior
The abruptio placenta is the premature separation of the placenta from the uterus, and in most cases, the patient suffers vaginal bleeding, abnormality uterine contractions, and fetal distress.
Placenta Accreta

Placenta Accreta
Placenta Accreta
The placenta accreta is a severe complications in obstetric case, which involves abnormal deep attachment of the placenta from endometrium and into the myometrium. Most pregnant mother, suffering from placenta accreta is in higer risk of fatality because of severe bleeding or hemorrhage during the removal of the placenta, thus, in the case of placenta accreta, surgery is required in removing the placenta.
18) Abortion (Murdering the fetus inside the mother’s womb)

Abortion is murdering the fetus inside the womb

Abortion
Abortion is the termination of pregnancy or expulsion from the uterus or embryo or purpose of inducing using tools such as vacuum, sharpened tools, drinking herbal plants, and other methods used by illegal abortionists. It is sometimes called miscarriage or “unintentional abortion”. Abortion is considered a murder, killing an innocent fetus is a murder and infanticide case.
19) Miscarriage (premature birth)
Miscarriage or premature birth

Miscarriage or miscarried
Miscarriage is an “unintentional abortion”, sometimes the fetus are not stable, healthy or very fragile inside the womb.
Still Birth or Still Born ( died inside the womb)
Still born o still birth

Still born baby
Stillbirth occurs when the fetus died inside the uterus after 20 weeks of gestation or when the fetus weigh only 400 grmas or 14 oz. After the fetus died inside the womb, the expectant mother will no longer have contractions and give a normal childbirth, and this is also called miscarriage.
20) Preterm Birth or Premature Birth
Premature Baby

Premature Baby
The preterm birth, commonly called premature birth referring to babies prematurely born less than 37 weeks of gestational age. Preterm birth are very elusive and of unknown causes. But in some cases, expectant mothers with unhealthy conditions and sometimes heavy smoker mother makes their baby smaller and thinner, and could trigger to giving birth prematurely.
